Generally speaking, a D/E ratio below 1 would be seen as relatively safe, whereas values of 2 or higher might be considered risky. Companies in some industries, such as utilities, consumer staples, and banking, typically have relatively high D/E ratios. As a rule, short-term debt tends to be cheaper than long-term debt and is less sensitive to shifts in interest rates, meaning that the second company’s interest expense and cost of capital are likely higher. If interest rates are higher when the long-term debt comes due and needs to be refinanced, then interest expense will rise. A debt to equity ratio of 0.25 shows that the company has 0.25 units of long-term debt for each unit of owner’s capital. Next, find the shareholders’ equity section on the balance sheet and sum the listed items to find the total shareholders’ equity.
Other Related Ratios for Specific Uses
This works using Wisesheets formulas which allow you to retrieve tons of financial data, dividend data, price data and more for over 50k securities worldwide. If you want to express it as a percentage, you must multiply the result by 100%. In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about the D/E ratio to help you make better financial decisions. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
What does a negative D/E ratio mean?
- A higher debt-to-income ratio could be more risky in an economic downturn, for example, than during a boom.
- By learning to calculate and interpret this ratio, and by considering the industry context and the company’s financial approach, you equip yourself to make smarter financial decisions.
- For example, if a company, such as a manufacturer, requires a lot of capital to operate, it may need to take on a lot of debt to finance its operations.
- If a company’s D/E ratio is too high, it may be considered a high-risk investment because the company will have to use more of its future earnings to pay off its debts.
In order to calculate the debt-to-equity ratio, you need to understand both components. For comparison of two or more companies, analyst should obtain the ratio of only those companies whose business models are the same and that directly compete with each other within the industry. That’s when my team and I created Wisesheets, a tool designed to automate the stock data gathering process, with the ultimate goal of helping anyone quickly find good investment opportunities. It is a problematic measure of leverage, because an increase in non-financial liabilities reduces this ratio.[3] Nevertheless, it is in common use.
Do you own a business?
✝ To check the rates and terms you may qualify for, SoFi conducts a soft credit pull that will not affect your credit score. It’s easy to get started when you open an investment account with SoFi Invest. You can invest in stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, alternative funds, and more.
Quick Links
However, it could also mean the company issued shareholders significant dividends. However, a low D/E ratio is not necessarily a positive sign, as the company could be relying too much on equity financing, which is costlier than debt. The D/E ratio represents the proportion of financing that came from creditors (debt) versus shareholders (equity). Publicly traded companies that are in the midst of repurchasing stock may also want to control their debt-to-equity ratio. That’s because share buybacks are usually counted as risk, since they reduce the value of stockholder equity.
How to use the D/E Ratio in conjunction with other financial ratios for comprehensive analysis
The D/E Ratio is also crucial for comparing companies within the same industry. Different industries have different capital structures and financing norms, making it essential to compare a company’s debt-to-equity ratio against industry averages and benchmarks. This comparison provides valuable context, helping investors and analysts determine whether a company’s leverage is in line with industry standards or if it stands out as an outlier. The Debt to Equity ratio is a financial metric that compares a company’s total debt to its shareholder equity.
Lack of performance might also be the reason why the company is seeking out extra debt financing. The debt to equity ratio is calculated by dividing total what is a yodlee bank feed in xero liabilities by total equity. The debt to equity ratio is considered a balance sheet ratio because all of the elements are reported on the balance sheet.
Banks carry higher amounts of debt because they own substantial fixed assets in the form of branch networks. Higher D/E ratios can also tend to predominate in other capital-intensive sectors heavily reliant on debt financing, such as airlines and industrials. If a company has a negative D/E ratio, this means that it has negative shareholder equity. In most cases, this would be considered a sign of high risk and an incentive to seek bankruptcy protection. What counts as a “good” debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio will depend on the nature of the business and its industry.
Banks often have high D/E ratios because they borrow capital, which they loan to customers. At first glance, this may seem good — after all, the company does not need to worry about paying creditors. If a D/E ratio becomes negative, a company may have no choice but to file for bankruptcy. If the D/E ratio of a company is negative, it means the liabilities are greater than the assets. They may note that the company has a high D/E ratio and conclude that the risk is too high. For this reason, it’s important to understand the norms for the industries you’re looking to invest in, and, as above, dig into the larger context when assessing the D/E ratio.
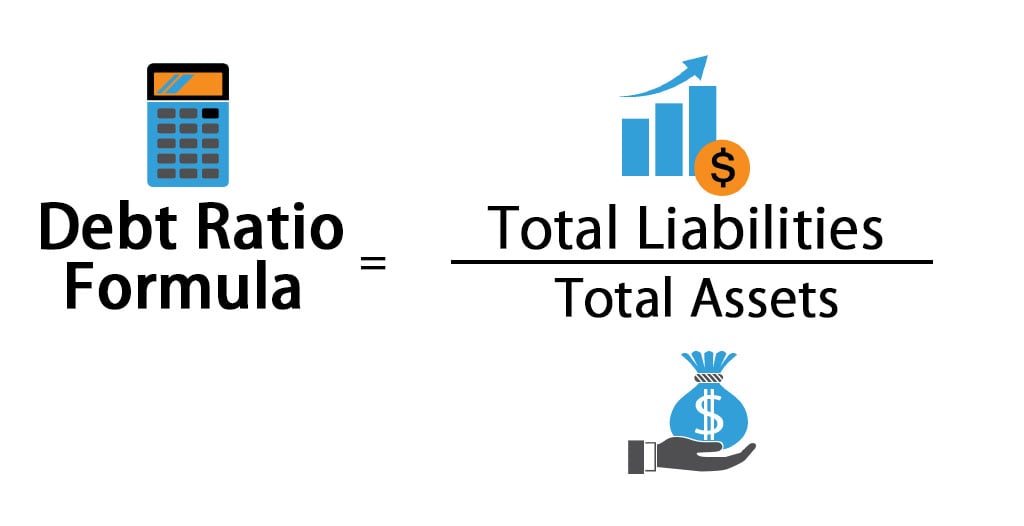
This looks at the total liabilities of a company in comparison to its total assets. On the surface, this may sound like the debt ratio formula is the same as the debt-to-equity ratio formula. However, the total debt ratio formula includes short-term assets and liabilities as part of the equation, which the debt-to-equity ratio discounts.
Debt to equity ratio is calculated by dividing total liabilities by stockholder’s equity. Companies can manage their Debt to Equity ratio by controlling debt levels and increasing equity through retained earnings or issuing new shares. Strategic management of this ratio is crucial for long-term financial health. The D/E ratio illustrates the proportion between debt and equity in a given company.
